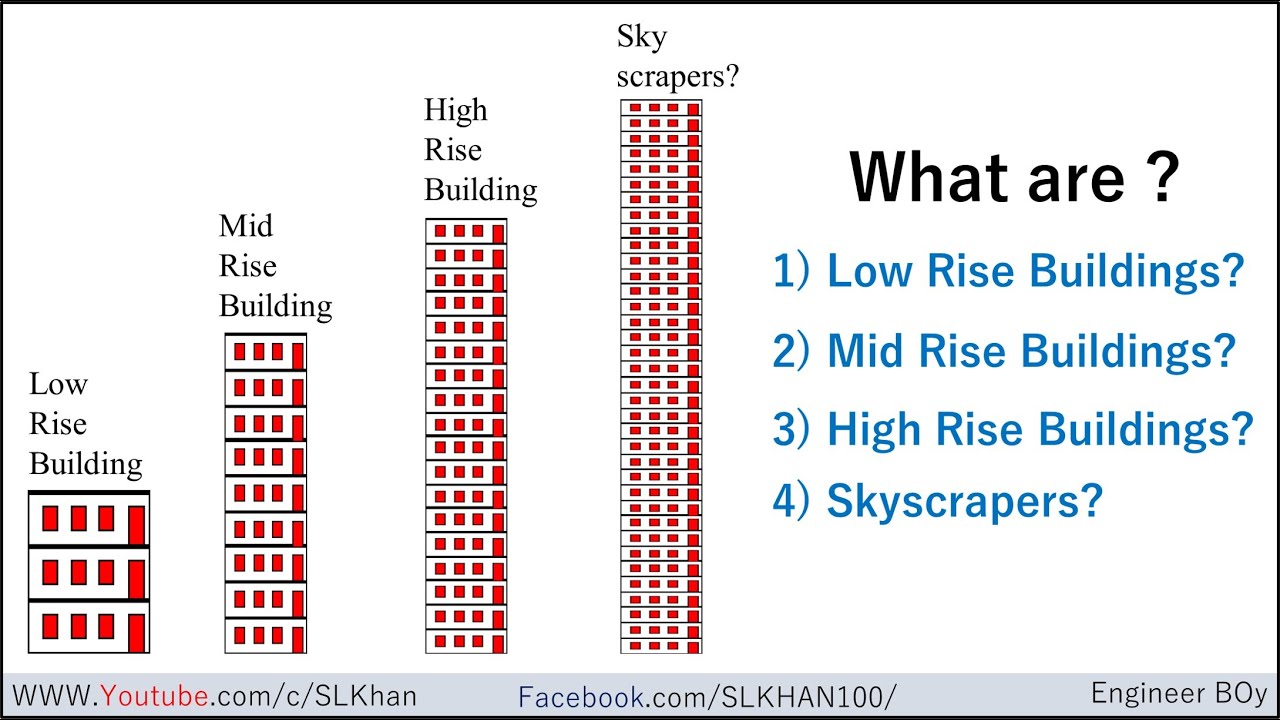
A low rise building is a term frequently used in urban planning and architecture to describe structures that are relatively short in height compared to their taller counterparts. These buildings typically have fewer stories, usually ranging from one to four or five, and occupy less vertical space. The definition of low rise buildings can vary slightly depending on regional and zoning laws, but the overarching characteristics remain relatively consistent across different areas. In a world dominated by skyscrapers and high-rise developments, low rise buildings maintain their relevance for various reasons, such as their affordability, accessibility, and community-focused designs. They often blend well into residential neighborhoods, providing a sense of scale that feels inviting and familiar.
The growing trend towards sustainable and eco-friendly architecture has also increased the interest in low rise buildings. These structures can be designed to minimize environmental impact, often making use of local materials and energy-efficient systems. With the rise of telecommuting and urban sprawl, many people are now seeking homes and workplaces that offer a balance between convenience and a sense of community.
In this article, we will delve deeper into the definition of low rise buildings, explore their advantages and disadvantages, and discuss their role in modern urban landscapes. Understanding the low rise building definition is essential for anyone involved in real estate, architecture, or urban planning, as it provides insights into how these structures can shape our communities.
What is the Low Rise Building Definition?
The low rise building definition encompasses a variety of structures, but primarily refers to buildings that do not exceed a certain height limit, typically set by local zoning regulations. These buildings are designed with a focus on human scale, often enhancing the livability of neighborhoods.
Why Are Low Rise Buildings Important?
Low rise buildings play a significant role in urban development. They provide essential housing options, commercial spaces, and community facilities while maintaining a lower density than high-rise buildings. Some key reasons why they are crucial include:
- Community Integration: They encourage social interaction and foster a sense of belonging.
- Affordability: Generally, they are more cost-effective to construct and maintain.
- Accessibility: With fewer floors, they are easier to navigate for people of all ages and abilities.
- Environmental Impact: They can be designed to be energy-efficient, using fewer resources compared to larger structures.
How Do Low Rise Buildings Differ from Other Types of Structures?
To understand the low rise building definition, it is essential to differentiate these structures from mid-rise and high-rise buildings. Typically, mid-rise buildings range from six to twelve stories, while high-rise buildings exceed twelve stories. The primary differences lie in their height, density, and design considerations.
What Are the Advantages of Low Rise Buildings?
Low rise buildings offer various advantages that make them appealing to homeowners, developers, and urban planners alike. Some of the most notable benefits include:
- Enhanced Community Feel: They contribute to a more intimate neighborhood atmosphere.
- Lower Construction Costs: They generally cost less to build due to their size and complexity.
- Improved Safety: In emergencies, low rise buildings can be safer as they are easier to evacuate.
- Better Accessibility: They are often designed with ramps and features that cater to individuals with disabilities.
What Are the Disadvantages of Low Rise Buildings?
Despite their numerous advantages, low rise buildings do have some drawbacks. Consider the following points:
1. Limited Space: They may not be able to accommodate large populations or businesses.
2. Urban Sprawl: Increased low rise developments can contribute to sprawl, leading to longer commutes and infrastructure strain.
3. Potential for Inefficient Land Use: In some urban areas, low rise buildings may not maximize land use compared to higher structures.
How Does the Low Rise Building Definition Impact Urban Planning?
The low rise building definition has a significant impact on urban planning, as it influences zoning laws, land use policies, and community development strategies. Urban planners must take into account the benefits and limitations of these structures when designing neighborhoods and cities. They must balance the need for housing and commercial space with the desire for community-oriented environments.
What Are Some Examples of Low Rise Buildings?
Low rise buildings come in various forms and serve different purposes. Here are a few common examples:
- Single-family homes: These are the most common type of low rise buildings, featuring one to two stories.
- Duplexes and triplexes: Multi-family homes that provide housing for several families while maintaining a low profile.
- Townhouses: Row houses that often share walls but are designed with individual entrances.
- Small office buildings: Typically one to three stories, providing workspace without the height of a skyscraper.
How Do Low Rise Buildings Fit into Sustainable Development?
Low rise buildings align well with sustainable development goals. By focusing on smaller structures, developers can create more energy-efficient designs, reduce the carbon footprint of construction, and promote environmentally friendly living. Additionally, they often encourage walking and cycling, reducing reliance on cars and promoting healthier lifestyles.
What Does the Future Hold for Low Rise Buildings?
The future of low rise buildings looks promising as urban areas continue to evolve. With increasing urbanization and a growing emphasis on sustainability, low rise structures are likely to remain a vital component of city planning. As communities seek to create more livable spaces, the low rise building definition will continue to shape urban landscapes, ensuring that cities remain vibrant and accessible for all.
Article Recommendations
- Cuanto Pesa Donal Trump
- Gunsmoke Lijah
- Glenn Close Michael Douglas
- Reggie Mathis
- How Do You Spell Freckles
- Aj And Kandi Burruss
- What Happened To Adam Cartwright
- Chuck Drummond Died
- Why Did Jonathan Lamb Leave Daystar
- Ryan Paevey Birthday