The repeat measure sign is a crucial notation used in various fields, particularly in music and statistics. This symbol serves as a guide for musicians and analysts alike, helping them navigate complex compositions and data sets effectively. The repeat measure sign not only aids in improving the efficiency of performance but also enhances understanding and interpretation of repetitive patterns in music and data.
In music, the repeat measure sign instructs performers to repeat a section, ensuring that the intended emotional and rhythmic qualities are conveyed accurately. On the other hand, in statistics, it marks repeated measurements or trials, providing a clearer picture of variability and reliability in data analysis. This dual significance underscores its importance across different disciplines, illustrating how a simple symbol can have profound implications.
As we delve deeper into the concept of the repeat measure sign, we will explore its various applications, historical background, and even some practical tips for using it effectively. Whether you are a musician, a data analyst, or simply someone with an appreciation for the nuances of notation, this article aims to enlighten you on the significance of the repeat measure sign.
What is the Repeat Measure Sign?
The repeat measure sign consists of two vertical lines with a double bar line and is found in both music notation and statistical analysis. In music, it indicates that a particular segment of the score should be repeated, allowing performers to revisit a melody or harmony as intended by the composer. This sign ensures that listeners experience the full depth of the piece, as certain musical phrases often carry thematic weight that deserves repetition.
In statistical terms, the repeat measure sign denotes the occurrence of repeated measurements within a study. This is especially relevant in experiments where multiple observations are taken under similar conditions to gauge the reliability of results. By marking these repetitions, analysts can better understand trends and variations in their data, leading to more robust conclusions.
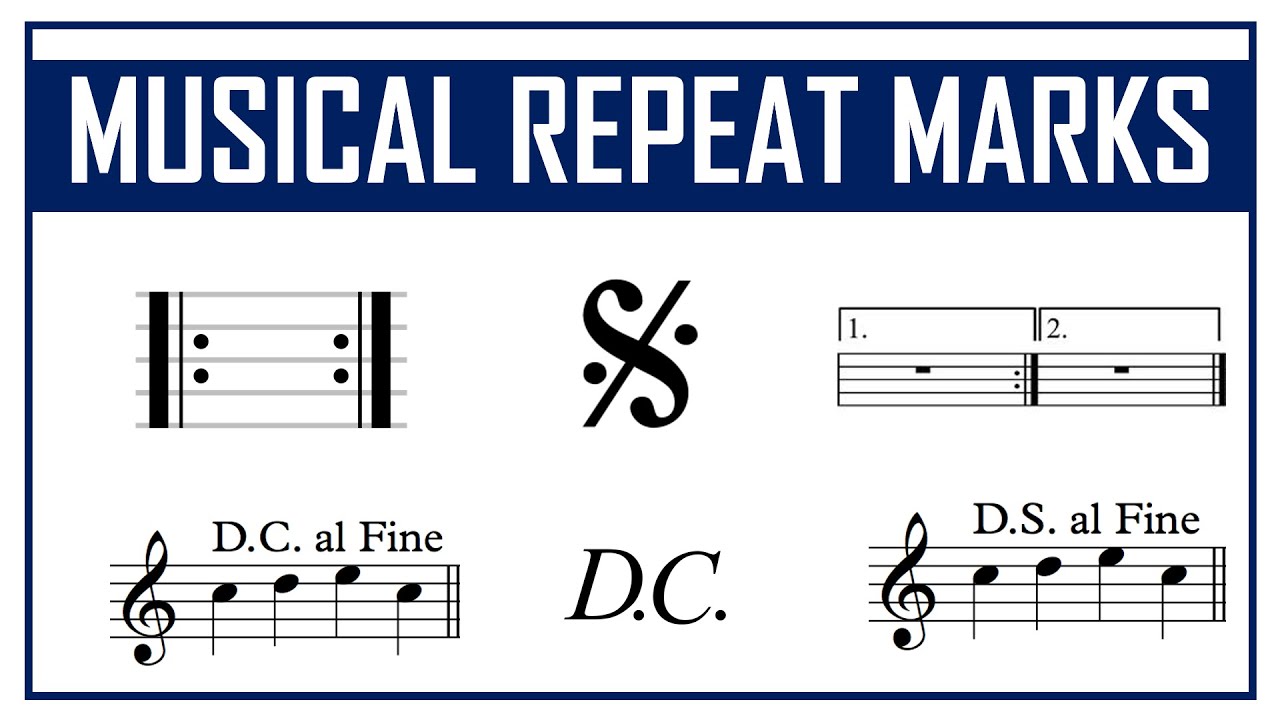
How is the Repeat Measure Sign Used in Music?
Musicians encounter the repeat measure sign frequently in sheet music. It serves several purposes:
- Emphasizing Key Themes: Repetition can underscore significant musical motifs, making them memorable for the audience.
- Creating Structure: It helps in organizing the music, providing a clear roadmap for performers.
- Enhancing Emotional Impact: Repeating certain sections can evoke deeper feelings and responses from the audience.
Understanding how to interpret the repeat measure sign effectively can enhance a musician's performance and overall musicality.
What are the Different Types of Repeat Measure Signs?
There are several variations of the repeat measure sign in music notation:
- Simple Repeat Sign: This is the standard repeat sign, instructing musicians to return to the beginning of the repeated section.
- First and Second Ending: This variation allows for the repetition of a section while providing different endings, creating a more dynamic musical experience.
- Dal Segno: This sign indicates a return to a specific point in the music, often marked by a symbol resembling an "S" with a line through it.
How is the Repeat Measure Sign Used in Statistics?
In the realm of statistics, the repeat measure sign plays a vital role in experimental design and data analysis. It is commonly used in repeated measures ANOVA, a statistical method that allows researchers to analyze the differences between groups when the same subjects are involved in multiple measurements.
What are the Advantages of Using Repeat Measures?
The use of repeat measures offers several benefits:
- Increased Statistical Power: By analyzing the same subjects multiple times, researchers can detect smaller differences with greater confidence.
- Control Over Variability: This method helps control for individual differences, leading to more reliable results.
- Cost-Effective: Using the same subjects reduces the need for larger sample sizes, saving time and resources.
What Challenges are Associated with Repeat Measures?
While repeat measures provide valuable insights, they also come with challenges:
- Learning Effects: Subjects may perform differently due to practice or familiarity with the task, influencing results.
- Fatigue: Repeated testing can lead to fatigue, impacting performance and data quality.
- Time Constraints: Conducting multiple measurements requires careful planning and time management.
Conclusion: The Impact of the Repeat Measure Sign
The repeat measure sign holds significant value in both music and statistics, bridging the gap between artistic expression and analytical rigor. Whether guiding musicians through complex compositions or helping researchers draw meaningful conclusions from their data, this simple yet powerful symbol is integral to effective communication in both fields.
By understanding its applications and implications, individuals can harness the full potential of the repeat measure sign in their respective practices, enriching their experiences and outcomes. As we continue to explore the nuances of notation and measurement, the repeat measure sign will undoubtedly remain a key player in the landscapes of music and science.
Article Recommendations
- Birthday January 16 Astrologyl
- Dianna Williams Bring It
- The Prince Of Denmark
- Which Shark Vacuum Is Better
- John Gaines Height
- Gainbridge Fieldhouse Player Crossword
- Gunsmoke Lijah
- Sean Mcdermott 9 11 Quote
- How Did Rudolph The Red Nosed Reindeer Originated
- Don Trump Je Ex Wife