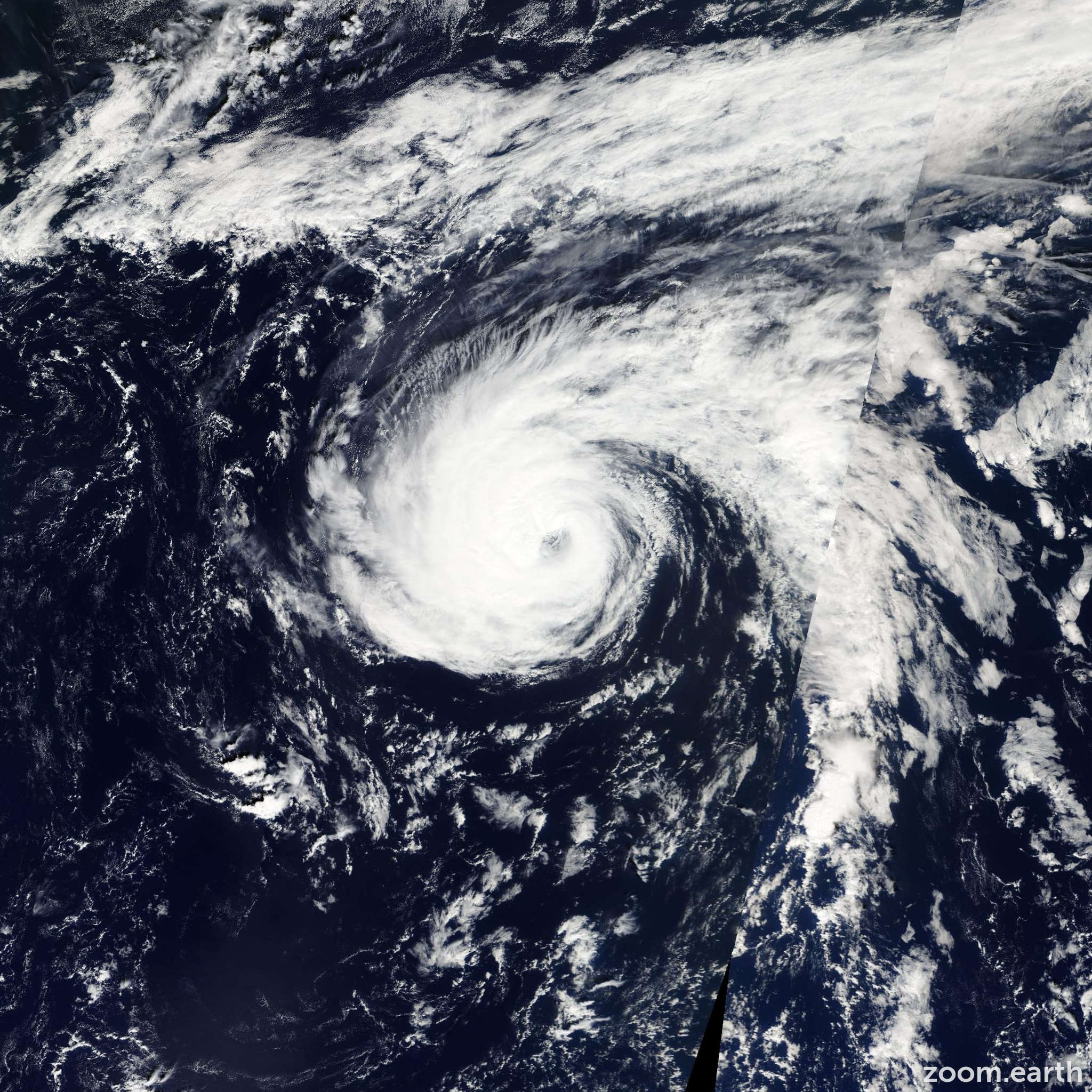
Hurricane Nadine has become a significant topic of discussion in the realm of meteorology and climate studies. This powerful storm has captured the attention of experts and the general public alike due to its unusual trajectory and intensity. In this article, we will delve deep into the details surrounding Hurricane Nadine, including its formation, impact, and the science behind hurricanes in general.
This article will not only provide a detailed account of Hurricane Nadine but will also serve as an educational resource for those looking to understand the broader implications of such weather phenomena. With that said, let’s dive into the specifics of Hurricane Nadine, including its formation, path, impact, and the lessons learned from its occurrence.
Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction to Hurricane Nadine
- 2. Biography of Hurricane Nadine
- 3. Formation of Hurricane Nadine
- 4. Path and Trajectory of Hurricane Nadine
- 5. Impact of Hurricane Nadine
- 6. Scientific Analysis of Hurricane Nadine
- 7. Comparison with Other Hurricanes
- 8. Conclusion
1. Introduction to Hurricane Nadine
Hurricane Nadine formed in the Atlantic Ocean during the hurricane season, which typically runs from June 1 to November 30 in the Northern Hemisphere. This storm was notable for its longevity and the unique patterns it displayed. As we examine Hurricane Nadine, we will assess its lifecycle, from tropical depression to a full-blown hurricane.
Understanding the structure and behavior of hurricanes is essential for preparedness and response. Nadine serves as a case study in the complexities of weather patterns and the influence of atmospheric conditions. This section will set the stage for a deeper analysis of Hurricane Nadine.
2. Biography of Hurricane Nadine
| Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Name | Nadine |
| Formation Date | September 11, 2012 |
| Peak Intensity | Category 1 Hurricane |
| Duration | 15 days |
| Areas Affected | Azores, Portugal, parts of the Eastern United States |
3. Formation of Hurricane Nadine
Hurricane Nadine originated from a tropical wave that moved across the Atlantic Ocean. As atmospheric conditions became favorable, the storm began to develop. The process of hurricane formation involves several key factors:
- Warm ocean waters (at least 26.5°C or 80°F)
- Low vertical wind shear
- High humidity in the mid-troposphere
- Pre-existing weather disturbance
These conditions led to the development of Nadine, transforming it from a tropical depression into a hurricane within a short time frame. Understanding these elements can help us predict future storms and mitigate their impacts.
4. Path and Trajectory of Hurricane Nadine
Hurricane Nadine followed a complex path that is often characteristic of storms in the Atlantic. After forming, it moved northwest before eventually turning back towards the northeast. This unusual trajectory impacted various regions, leading to precautionary measures and evacuations in some areas.
Tracking the path of hurricanes is crucial for forecasting and preparedness. Meteorologists use satellite imagery and weather models to predict a storm's movement and potential impact.
5. Impact of Hurricane Nadine
The impact of Hurricane Nadine was felt across multiple regions, with significant effects on the environment and local communities. Some key impacts included:
- Heavy rainfall and flooding in affected areas
- Wind damage to infrastructure
- Evacuations in vulnerable regions
- Economic repercussions for businesses and local economies
Understanding the impact of Hurricane Nadine helps us to appreciate the resilience required in the face of natural disasters and the importance of effective emergency response strategies.
6. Scientific Analysis of Hurricane Nadine
Scientists have studied Hurricane Nadine extensively to understand its dynamics and behavior. Key areas of focus include:
- The role of climate change in altering hurricane patterns
- Comparative studies with other hurricanes
- Long-term environmental effects of hurricane activity
These analyses contribute to a growing body of knowledge that can inform future hurricane preparedness and response efforts.
7. Comparison with Other Hurricanes
When compared to other hurricanes, Nadine exhibited some unique characteristics. For instance, its long duration and erratic path were notable. Comparing Nadine with storms like Hurricane Sandy and Hurricane Katrina provides valuable insights into the variability of hurricane behavior.
Such comparisons can help researchers identify patterns and trends that are crucial for predicting future storms and preparing for their impacts.
8. Conclusion
In summary, Hurricane Nadine serves as a significant case study in understanding hurricane formation, behavior, and impact. By exploring its lifecycle and the factors contributing to its development, we can enhance our preparedness for future storms.
As we continue to face the challenges posed by climate change and extreme weather events, it is essential to remain informed and proactive in our response strategies. We encourage readers to share their thoughts on Hurricane Nadine and engage with our community by leaving comments below.
Thank you for taking the time to explore the intricacies of Hurricane Nadine with us. We hope this article has provided valuable insights and encourages you to stay informed about weather phenomena and their impacts.
Article Recommendations
- Ribcage Straight Ankle Jeans
- Bob Evans
- John Krasinski Weight
- Matilda Today
- What Is Open On Xmas
- What Former Presidents Are Still Alive
- Is Shirley Caesar Alive Today
- What Nationality Is Nico Iamaleava
- Don Trump Je Ex Wife
- Cnn What Does Donal Trump Want To Do With Violence