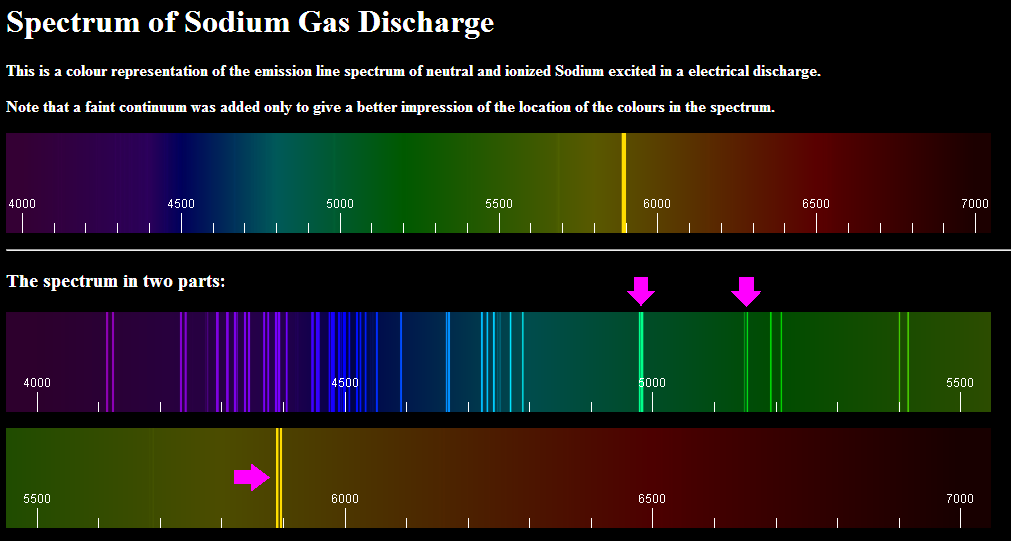
The sodium spectrum is a fascinating phenomenon that plays a crucial role in various scientific fields, including chemistry, astronomy, and physics. It refers to the characteristic patterns of light emitted by sodium atoms when they are excited by heat or electricity. This emission is not just a random occurrence; it reveals much about the atomic structure and energy levels of sodium. By studying the sodium spectrum, scientists can gain insights into the elemental composition of stars, analyze chemical substances, and understand more about the universe around us.
When sodium gas is heated or energized, it produces a series of bright lines in specific wavelengths on a spectroscopic scale. These bright lines correspond to the transitions of electrons between different energy levels within the sodium atoms. The distinct yellow color of sodium lamps, commonly used in street lighting, is a result of this emission spectrum. Understanding the sodium spectrum can help us grasp the fundamental principles of light emission and absorption in atoms.
As we dive deeper into the sodium spectrum, we will explore its significance across various scientific disciplines, the specific wavelengths it encompasses, and the applications it finds in both practical and theoretical contexts. From enhancing our understanding of chemical reactions to illuminating the night sky, the sodium spectrum holds a wealth of knowledge waiting to be explored.
What is the Sodium Spectrum?
The sodium spectrum is essentially the range of wavelengths emitted by sodium when it is energized. Most commonly, it is characterized by a pair of yellow lines known as the D-lines, located at approximately 589.0 nm and 589.6 nm. These lines occur due to electronic transitions in the sodium atom, specifically the transition of electrons between energy levels.
How is the Sodium Spectrum Produced?
The production of the sodium spectrum occurs when sodium atoms absorb energy, causing their electrons to jump to higher energy levels. When the electrons return to their original energy levels, they release energy in the form of light. This process can be stimulated through methods such as heating sodium in a flame or passing an electric current through a sodium vapor. The emitted light can then be analyzed using a spectrometer to reveal the distinct lines of the sodium spectrum.
Why is the Sodium Spectrum Important in Astronomy?
The sodium spectrum holds immense importance in the field of astronomy. Astronomers use the sodium lines to analyze the composition of stars and celestial bodies. By examining the absorption and emission lines in the spectrum of distant stars, scientists can determine the presence of sodium and other elements, leading to insights into the star's age, temperature, and chemical makeup.
What are the Applications of the Sodium Spectrum?
The sodium spectrum finds applications in various fields due to its unique properties. Some of the key applications include:
- Street Lighting: Sodium vapor lamps are widely used for street lighting due to their efficiency and the distinct yellow light they emit.
- Chemical Analysis: The sodium spectrum can be used in spectroscopic techniques to identify sodium in chemical samples.
- Research in Physics: The study of the sodium spectrum helps in understanding atomic and molecular structures.
- Astronomical Studies: It provides critical data for analyzing stellar compositions and distances.
How Does the Sodium Spectrum Compare to Other Elemental Spectra?
Every element has a unique spectrum, characterized by distinct wavelengths corresponding to various electronic transitions. Compared to other spectra, the sodium spectrum is notable for its simplicity and the prominence of its D-lines. For instance, the hydrogen spectrum consists of several lines in the visible range, but the sodium spectrum is more limited yet highly recognizable. This uniqueness makes the sodium spectrum particularly useful for educational purposes and practical applications.
What Role Does the Sodium Spectrum Play in Chemical Education?
In chemical education, the sodium spectrum is often one of the first spectra students encounter. It serves as an excellent example for demonstrating key concepts such as atomic structure, electron transitions, and spectroscopy. By observing the sodium D-lines, students can develop a foundational understanding of how elements interact with light and how this interaction can be measured and analyzed.
Can the Sodium Spectrum Be Used for Environmental Monitoring?
Yes, the sodium spectrum can be utilized in environmental monitoring. By analyzing the light emitted from sodium vapor lamps, researchers can assess the impact of artificial lighting on ecosystems. Additionally, the sodium spectrum can aid in monitoring sodium levels in various environments, which is particularly relevant in areas where sodium contamination may occur.
What Future Research Opportunities Exist for the Sodium Spectrum?
The sodium spectrum continues to present opportunities for research and discovery. Future studies may delve into:
- Improving the efficiency and design of sodium vapor lamps.
- Exploring the connections between sodium and other elements in stellar environments.
- Investigating the effects of sodium emissions on atmospheric chemistry.
In conclusion, the sodium spectrum is a vibrant and essential aspect of scientific inquiry that bridges multiple disciplines. From its role in illuminating our streets to its significance in understanding the cosmos, the sodium spectrum is an enduring topic of exploration, offering insights into both the microscopic and macroscopic worlds. By appreciating its characteristics and applications, we can unlock further mysteries and harness the potential of this fascinating phenomenon.
Article Recommendations
- Jerry Lorenzo Dad
- Bob Evans
- Laura Von Lindholm Playboy
- Lee Soo Hyuk Kim Min Hee
- New Year Movie 2024
- Cuanto Pesa Donal Trump
- The Prince Of Denmark
- Coincidencias Con Donal Trump
- Glitter And Gold Theme Party
- John Krasinski Weight