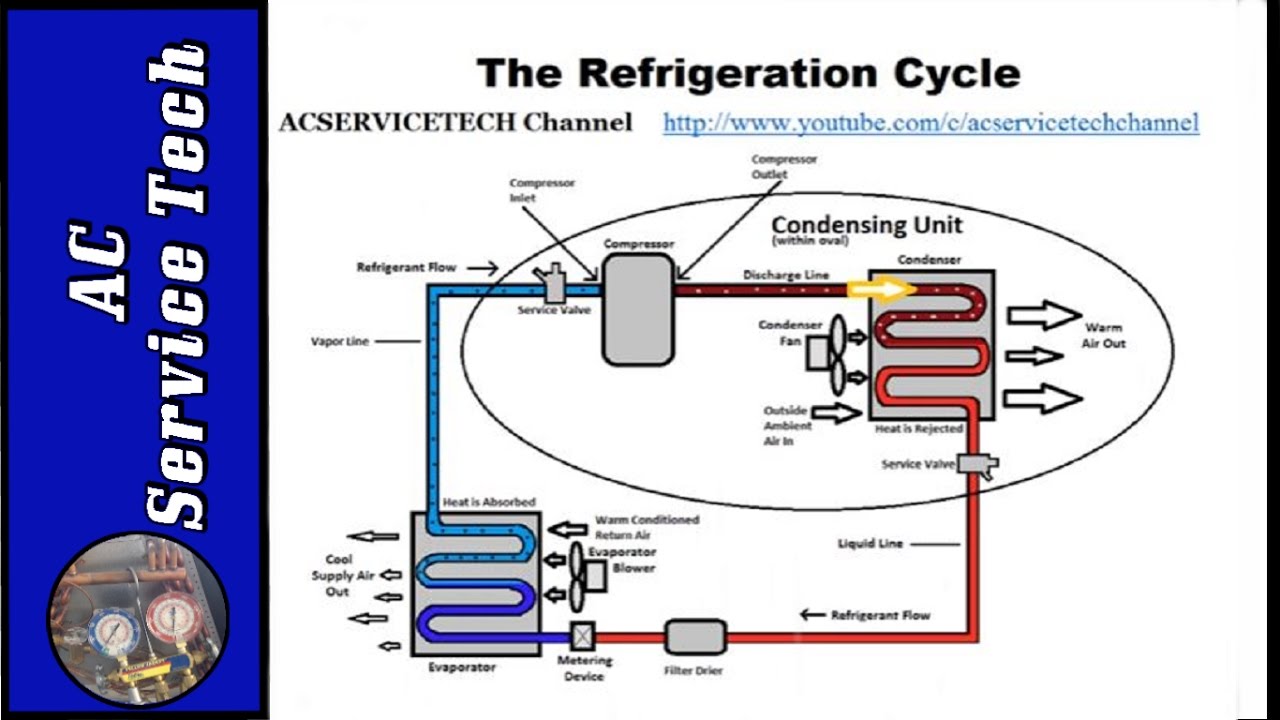
High subcooling means a critical concept in the field of thermodynamics and refrigeration. It refers to the process of cooling a liquid refrigerant below its saturation temperature without causing it to change into a vapor. This concept is essential for enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of cooling systems, ensuring that they operate optimally. In this article, we will delve deeper into what high subcooling means, its benefits, and its applications in various industries.
In the world of HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) and refrigeration, understanding high subcooling is vital for professionals and engineers. The efficiency of cooling systems can significantly impact energy consumption and operational costs. By employing high subcooling techniques, systems can achieve better performance and longevity. Moreover, this concept is increasingly relevant in today's quest for sustainable and energy-efficient solutions.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of high subcooling means, discussing its principles, applications, and advantages. We will also explore the science behind subcooling and how it relates to thermodynamic cycles. Whether you are a seasoned HVAC professional or a curious learner, this article will equip you with the knowledge necessary to understand and apply high subcooling in various contexts.
Table of Contents
- What is High Subcooling?
- Importance of Subcooling in Cooling Systems
- Principles of High Subcooling
- Applications of High Subcooling in Industries
- Benefits of High Subcooling
- How to Measure Subcooling
- Common Mistakes in Subcooling
- Conclusion
What is High Subcooling?
High subcooling refers to the process of reducing the temperature of a liquid refrigerant below its saturation point while maintaining it in a liquid state. This cooling process is crucial in refrigeration cycles as it helps in maximizing the efficiency of the cooling system. In a refrigeration cycle, a refrigerant absorbs heat from the environment and evaporates into vapor. However, before it can be re-condensed into a liquid, it must be subcooled to ensure that no vapor enters the condenser, which can lead to inefficiencies.
Definition of Subcooling
Subcooling is defined as the difference between the saturation temperature of the refrigerant at a given pressure and its actual temperature. For instance, if the saturation temperature of refrigerant R-134a at 30 psi is 35°F and the actual temperature is 30°F, the subcooling is 5°F. The greater the subcooling, the more efficient the refrigerant cycle becomes.
Importance of Subcooling in Cooling Systems
The importance of subcooling in cooling systems cannot be overstated. It plays a vital role in improving the overall efficiency and reliability of refrigeration systems. Here are some reasons why subcooling is essential:
- Prevention of refrigerant vapor entering the condenser, which enhances heat exchange efficiency.
- Increased system efficiency, leading to lower energy consumption.
- Improved performance during peak load conditions.
- Extended lifespan of the compressor and other system components.
Principles of High Subcooling
The principles of high subcooling are based on the laws of thermodynamics and fluid mechanics. When refrigerants are subcooled, they can absorb more heat from the environment, making them more effective in the cooling cycle. The main principles include:
- Heat Transfer: Enhanced heat transfer occurs in the condenser when the refrigerant is subcooled.
- Pressure and Temperature Relationship: The relationship between pressure and temperature in refrigerants dictates that lowering the temperature increases the efficiency of the cycle.
- Thermodynamic Cycles: Understanding the thermodynamic cycles (Carnot cycle, vapor-compression cycle) helps in optimizing subcooling processes.
Applications of High Subcooling in Industries
High subcooling is utilized in various industries, particularly in HVAC and refrigeration applications. Here are some key areas of application:
- Commercial Refrigeration: Supermarkets and convenience stores use high subcooling to maintain optimal temperatures in refrigerated display cases.
- Air Conditioning Systems: Residential and commercial air conditioning units employ subcooling to enhance cooling performance and efficiency.
- Industrial Processes: Manufacturing facilities often use high subcooling in processes where precise temperature control is necessary.
Benefits of High Subcooling
Implementing high subcooling practices offers several benefits, including:
- Improved energy efficiency, resulting in lower operational costs.
- Enhanced cooling performance, providing comfort in residential and commercial environments.
- Increased reliability and longevity of cooling systems.
- Reduced environmental impact through lower energy consumption.
How to Measure Subcooling
Measuring subcooling is essential for optimizing cooling systems. Here’s how to do it:
- Determine the saturation temperature of the refrigerant using pressure-temperature charts.
- Measure the actual temperature of the refrigerant at the condenser outlet.
- Calculate subcooling by subtracting the actual temperature from the saturation temperature.
Common Mistakes in Subcooling
While implementing high subcooling, it’s essential to avoid common mistakes that can lead to inefficiencies:
- Neglecting to check the refrigerant charge, which can affect subcooling performance.
- Ignoring the importance of proper airflow across the condenser coils.
- Failing to maintain the system, leading to potential refrigerant leaks.
Conclusion
High subcooling means a crucial concept in the HVAC and refrigeration industry that can significantly enhance the efficiency and performance of cooling systems. By understanding and applying the principles of high subcooling, professionals can improve energy efficiency, reduce operational costs, and extend the lifespan of equipment. It is essential to measure subcooling accurately and avoid common mistakes to achieve optimal system performance.
We encourage readers to share their experiences or questions regarding high subcooling in the comments below and explore other informative articles on our site.
Thank you for reading! We hope to see you back for more insightful articles.
Article Recommendations
- What Nationality Is Nico Iamaleava
- Best Handheld Vacuum
- Josh Gates Dating Now
- Ideas For Duo Day
- Who Plays Ally In Austin And Ally
- Chuck Drummond Died
- Who Is Alan Greenspan
- Comunicado Donal Trump
- Trump Third Term
- Trent Williams Tattoos