Harakat Arabic plays a crucial role in the Arabic language, enhancing the clarity and pronunciation of words. These diacritical marks are essential for learners and fluent speakers alike, as they provide a deeper understanding of the language's phonetics. Without harakat, the beauty and nuances of Arabic can easily be lost, leading to potential misunderstandings.
The Arabic script is rich and complex, and harakat serve as an essential guide to reading and writing. They help indicate short vowels, consonant doubling, and other phonetic features that are not represented in the letters alone. For those new to the language, mastering harakat is a fundamental step toward fluency and comprehension. This article will explore the significance of harakat, their various forms, and how they aid in mastering Arabic pronunciation.
As we dive deeper into the world of harakat Arabic, we will also uncover how these markings have evolved over time and their impact on the Arabic language as a whole. Understanding harakat is not just about reading; it is about appreciating the cultural and historical context of the Arabic language, which has influenced many civilizations and continues to thrive today.
What are Harakat in Arabic?
Harakat are diacritical marks that appear above or below Arabic letters, indicating the correct pronunciation of words. They are vital for learners of the language as they provide guidance on how to articulate each letter accurately. Without these markings, many Arabic words could be pronounced incorrectly, altering their meanings entirely.
Why are Harakat Important?
The importance of harakat in Arabic cannot be overstated. Here are some key reasons why they are essential:
- They clarify the pronunciation of words.
- They help differentiate between similar-looking words.
- They are crucial for proper recitation of the Quran.
- They assist in language learning for non-native speakers.
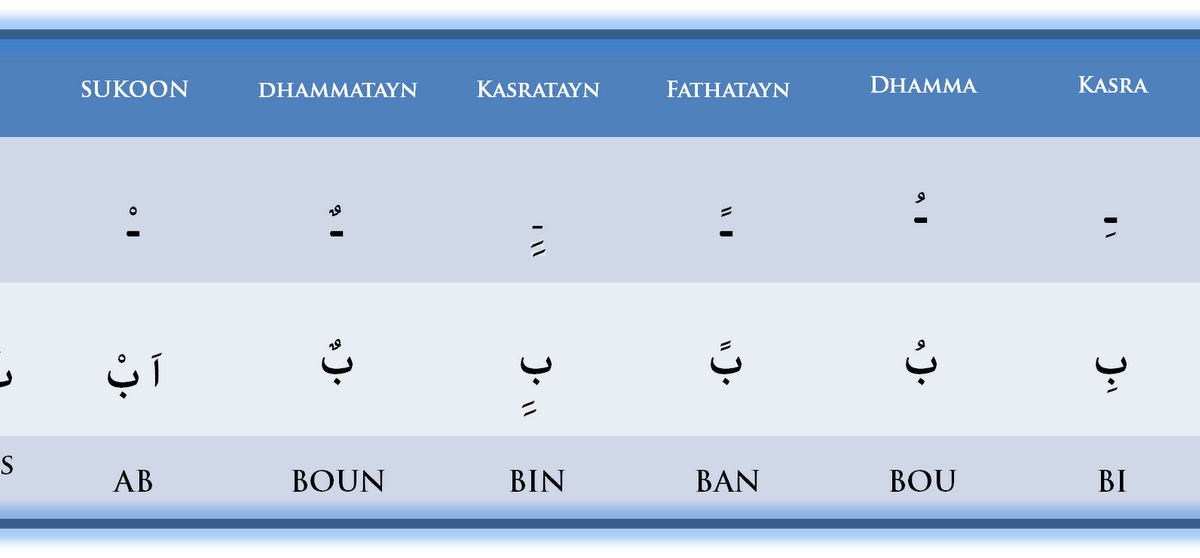
What are the Different Types of Harakat?
There are several types of harakat, each serving a unique purpose in the pronunciation of Arabic words. Here are the most common harakat:
- Fatha: A small diagonal line above a letter, indicating the short vowel 'a'.
- Damma: A small curl above a letter, indicating the short vowel 'u'.
- Kasra: A small diagonal line below a letter, indicating the short vowel 'i'.
- Shadda: A w-shaped mark above a letter, indicating that the consonant is doubled.
- Sukun: A small circle above a letter, indicating the absence of a vowel sound.
How Do Harakat Affect Arabic Language Learning?
For learners of Arabic, understanding harakat is crucial for several reasons:
- They aid in mastering pronunciation and fluency.
- They help learners understand the context of sentences.
- They provide a foundation for reading complex texts.
Can Harakat Change the Meaning of Words?
Yes, harakat can significantly alter the meaning of words. For instance, the word "كتب" (kataba) means "he wrote" with a fatha on the first letter. However, if pronounced without harakat, it could be interpreted differently. This highlights the importance of correctly using harakat in both written and spoken Arabic.
What Challenges Do Non-Native Speakers Face with Harakat?
Non-native speakers often encounter challenges when learning about harakat, including:
- Difficulty in recognizing the marks.
- Confusion over pronunciation variations.
- Struggles with reading fluency due to lack of practice.
How Can One Master Harakat in Arabic?
Mastering harakat requires practice and dedication. Here are some tips to help learners improve:
- Practice reading Arabic texts with harakat.
- Listen to native speakers and mimic their pronunciation.
- Engage in language exchange programs.
- Utilize educational resources and apps focused on Arabic language learning.
Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of Harakat Arabic
In conclusion, harakat Arabic represents a vital aspect of the Arabic language, enriching its phonetic structure and aiding in effective communication. Whether you are a native speaker or a learner, understanding and applying harakat is essential for mastering the nuances of Arabic. By embracing these diacritical marks, we can appreciate the beauty and complexity of this ancient language, ensuring its continued relevance in today's world.
Article Recommendations
- Is Shirley Caesar Alive Today
- Yk Osiris And Diddy
- Identify The Two Longest Rivers In The U S
- Cuanto Pesa Donal Trump
- The Prince Of Denmark
- Cnn What Does Donal Trump Want To Do With Violence
- Dorgi
- Who Is Slash Dating
- Reggie Mathis
- Glitter And Gold Theme Party